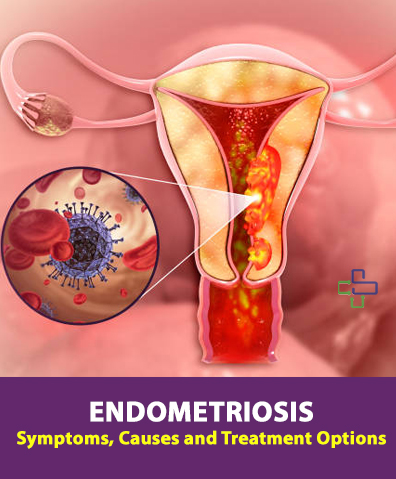
Endometriosis is a chronic, often painful disorder where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing inflammation, scar tissue, and, in some cases, infertility. Affecting more than 176 million women worldwide, it’s estimated that over 1 in 10 women may have this condition, but the actual number could be significantly higher due to underreporting, misdiagnosis, and a lack of accessible diagnostic methods. The condition is now recognized as one of the largest women’s health crises of our time. Here, we break down endometriosis symptoms, causes, effects, and treatment options to help increase understanding and support for those affected.
Common Symptoms of Endometriosis
Endometriosis symptoms vary, but common signs include:
- Severe menstrual cramps and pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Painful bowel movements or urination, especially during menstruation
- Heavy menstrual bleeding or spotting between periods
- Infertility (Endometriosis affects 30-50% of women facing infertility)
- Chronic fatigue and digestive issues like bloating and nausea
These symptoms can range from mild to severe and often worsen over time, making early diagnosis crucial.
Why Endometriosis Goes Undiagnosed for So Long
On average, it takes 7–10 years for endometriosis to be accurately diagnosed. This extended wait time can be attributed to factors like a lack of non-surgical diagnostic tools and a tendency in society to downplay or dismiss women’s pain. This delay can severely impact quality of life and fertility outcomes, as the condition often worsens without proper treatment.
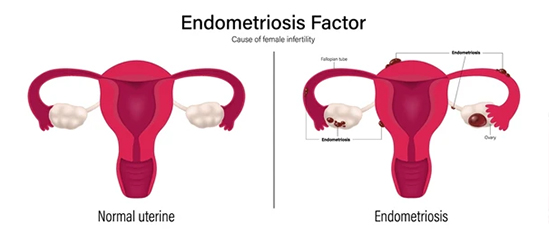
What Causes Endometriosis?
The exact cause of endometriosis remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Retrograde Menstruation: Menstrual blood flows back through the fallopian tubes into the pelvic cavity instead of leaving the body, allowing endometrial cells to grow outside the uterus.
- Genetics: Women with a family history of endometriosis are at higher risk, suggesting a genetic link.
- Immune System Disorders: A weakened immune system may fail to identify and destroy endometrial tissue growing outside the uterus.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Higher levels of estrogen can promote the growth of endometrial tissue.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins, like dioxins, may also increase the risk of endometriosis.
Understanding these causes can aid in prevention and help women recognize potential symptoms sooner.
Risk Factors: Family History & Genetic Links
Women who have a close relative with endometriosis are 2–3 times more likely to develop it themselves, highlighting a genetic component to the disorder. While researchers are working to better understand these genetic links, the heritable aspect means that women with family members affected by this should be especially vigilant about symptoms.
Effects of Endometriosis on Health and Lifestyle
The effects of endometriosis extend beyond physical pain, impacting various aspects of a woman’s life:
- Chronic Pain: Severe pain from endometriosis often limits daily activities, affecting productivity and overall well-being.
- Infertility: The condition can lead to blocked fallopian tubes, preventing egg and sperm from meeting. Up to half of the women with endometriosis face fertility challenges.
- Mental Health: Chronic pain and infertility struggles can lead to depression, anxiety, and stress.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Endometriosis can make it difficult to maintain a normal work-life balance, leading to missed days at work or school.
- Financial Strain: Treatment, pain management, and potential surgeries can impose a significant financial burden on women and their families.
Addressing these effects with timely treatment and support can help women manage the condition more effectively.
Economic and Productivity Impact
It isn’t just a physical and emotional burden; it also carries a significant economic impact. Studies estimate that women with endometriosis lose approximately 10 hours of productivity per week due to the condition. This has far-reaching implications, not only for the women affected but also for employers and healthcare systems globally.
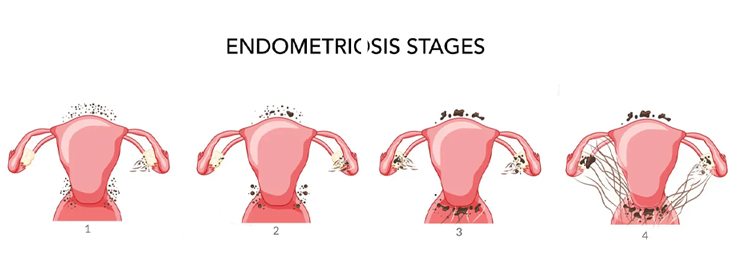
Stages of Endometriosis
The severity of endometriosis is classified into four stages by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine:
- Stage I (Minimal): Few, superficial implants with no scar tissue.
- Stage II (Mild): More extensive implants but limited scarring.
- Stage III (Moderate): Many deep implants and small cysts on ovaries.
- Stage IV (Severe): Large cysts, extensive scarring, and possible organ involvement.
The staging helps doctors create a tailored treatment plan to manage symptoms effectively.
Treatment Options for Endometriosis
While there’s no cure for endometriosis, treatments are available to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or hormonal IUDs help manage symptoms by reducing or stopping menstrual flow.
- Pain Relief: NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, are commonly used for pain management.
- Surgery: In severe cases, laparoscopy is performed to remove endometrial tissue and cysts.
- Fertility Treatment: Assisted reproductive technologies like IVF can help women with endometriosis conceive.
Women should work closely with healthcare providers to determine the best treatment approach, which may combine medical, hormonal, and lifestyle modifications.
Myths and Facts:
Misconceptions surrounding endometriosis contribute to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Here are a few common myths debunked:
- Myth: Endometriosis pain is just “bad cramps.”
- Fact: Endometriosis pain is more intense and persistent than typical cramps.
- Myth: Pregnancy cures endometriosis.
- Fact: While pregnancy may relieve symptoms temporarily, it is not a cure.
- Myth: Endometriosis is rare.
- Fact: Endometriosis is widespread but underdiagnosed due to lack of awareness and accessible diagnostics.
Addressing Social Stigma and Raising Awareness
Endometriosis often goes undiscussed, leaving women feeling isolated and without support. Increased awareness, education, and resources can help reduce stigma, ensuring women receive the medical attention and community support they need.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Women’s Health with SimpleeKare Health
Endometriosis is more than just a “women’s health issue”; it’s a global crisis impacting millions. With increased awareness, proper diagnosis, and accessible treatment options, women can regain control over their health and lives.
At SimpleeKare Health, we understand the unique challenges of endometriosis and are dedicated to providing compassionate care. Our team of skilled gynecologists is here to support you on your health journey with personalized treatment plans and resources to help you manage this condition effectively.
Take control of your health—reach out to SimpleeKare Health to consult with our best gynecologists and discover treatment options that work for you.